Metals and engineering alloys have the highest κ c values due to their high resistance to cracks.
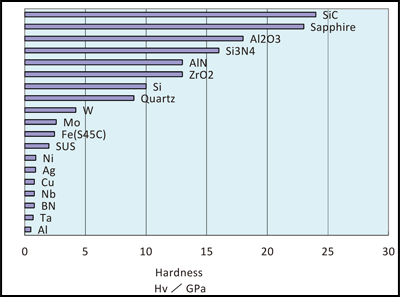
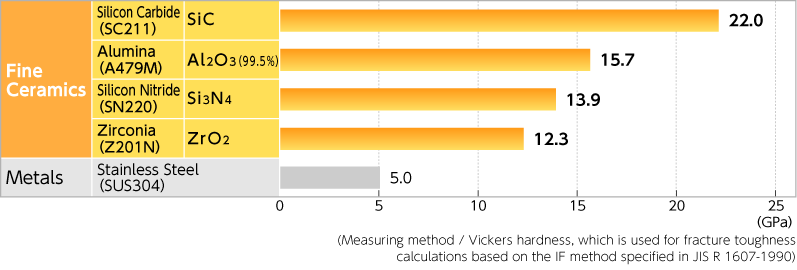
Hardness values for different metals ceramics and polymers.
Changes in student understanding of variability and their interest in experimental research will be explored.
The mohs hardness test is one of the earliest attempts at defining and comparing the hardness of mineral materials.
The mohs scale consists of values from 1 to 10 which correlate with the ability of the test material to withstand scratching by progressively harder minerals.
Primarily differences are due to their different chemical bonding properties homework 1.
The manufacture of ceramic components involves many different variables from the starting material and additives used to the forming method sintering process temperature and final finishing techniques as well as the size and shape of the part itself all of which affect the component s final property values.
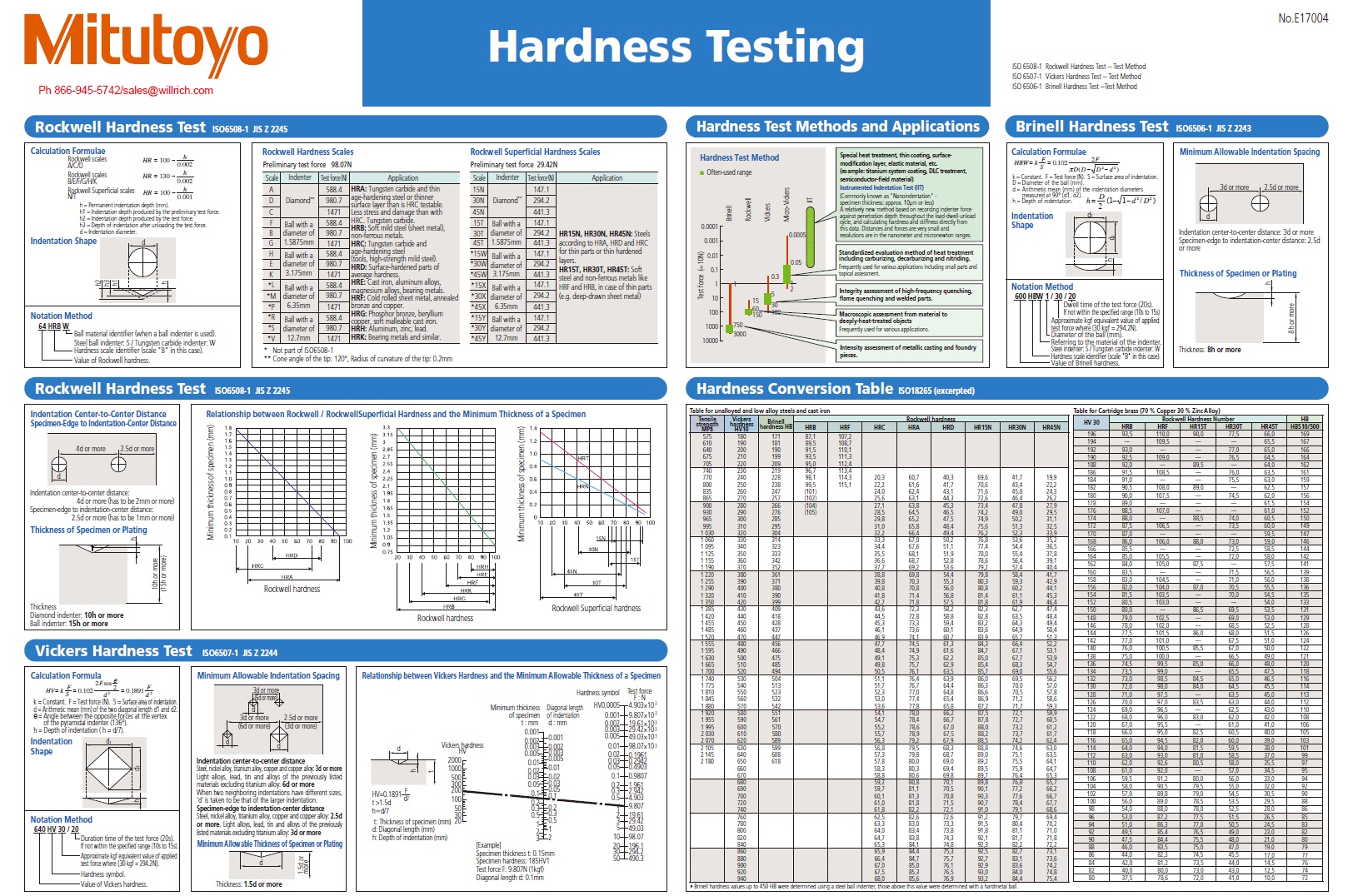
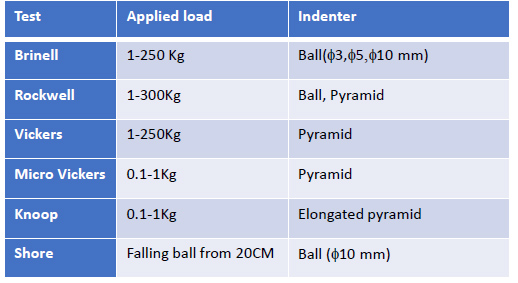
Background the engineering material property of hardness can be determined numerous ways to show wear.
Ceramics materials have high melting point therefore ceramics are used in furnace linings and other high.
It is typically used for geological purposes.
Fracture toughness in different materials.
Polymers cover different mechanical properties that include extensive levels of strength toughness and hardness.
Engineering ceramics have a relatively lower fracture toughness despite their higher strength.
The hardness and elastic modulus of picns including the pure polymer 0 on the x axis and dense ceramic 100 on the x axis were plotted in terms of ceramic ratio in fig.
Stress strain curves for metals ceramics and polymers objective we are interested about studying and comparing stress strain curves of metals ceramics and polymers.
There are mainly three types of polymers these are thermoplastics thermo setting and fiber reinforced plastics frps.